39 phase diagram of pure solvent and solution
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Phase_diagramPhase diagram - Wikipedia One type of phase diagram plots temperature against the relative concentrations of two substances in a binary mixture called a binary phase diagram, as shown at right. Such a mixture can be either a solid solution, eutectic or peritectic, among others. These two types of mixtures result in very different graphs. Solubility - Wikipedia In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.. The extent of the solubility of a substance in a specific solvent is generally measured as the concentration of the solute in a saturated solution, one in which no more …
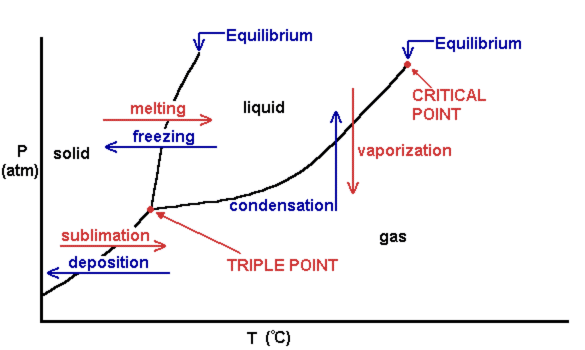
Supercritical fluid - Wikipedia Figures 1 and 2 show two-dimensional projections of a phase diagram.In the pressure-temperature phase diagram (Fig. 1) the boiling curve separates the gas and liquid region and ends in the critical point, where the liquid and gas phases disappear to become a single supercritical phase.. The appearance of a single phase can also be observed in the density …

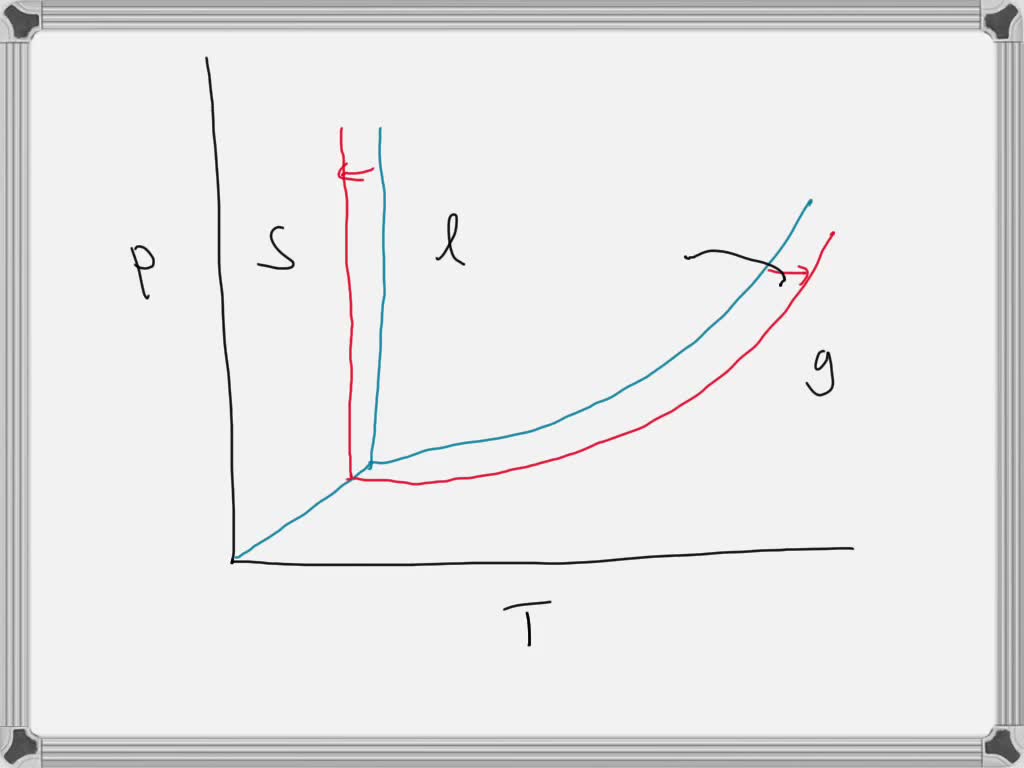
Phase diagram of pure solvent and solution
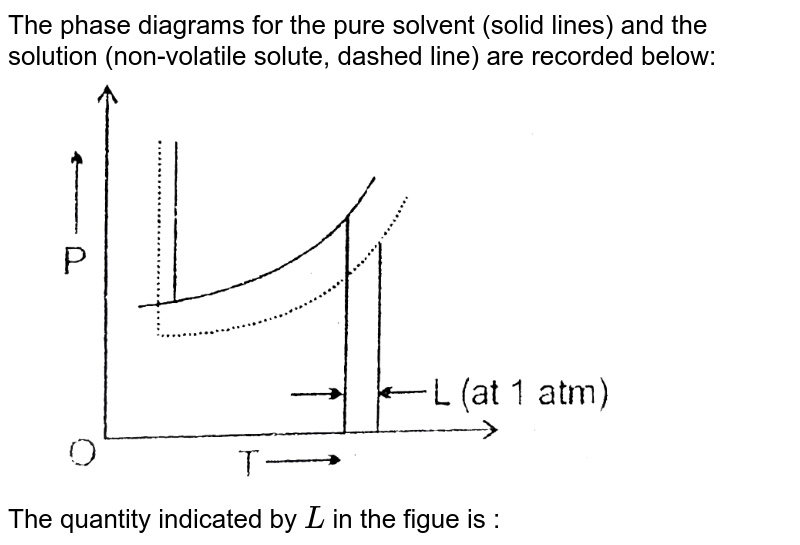
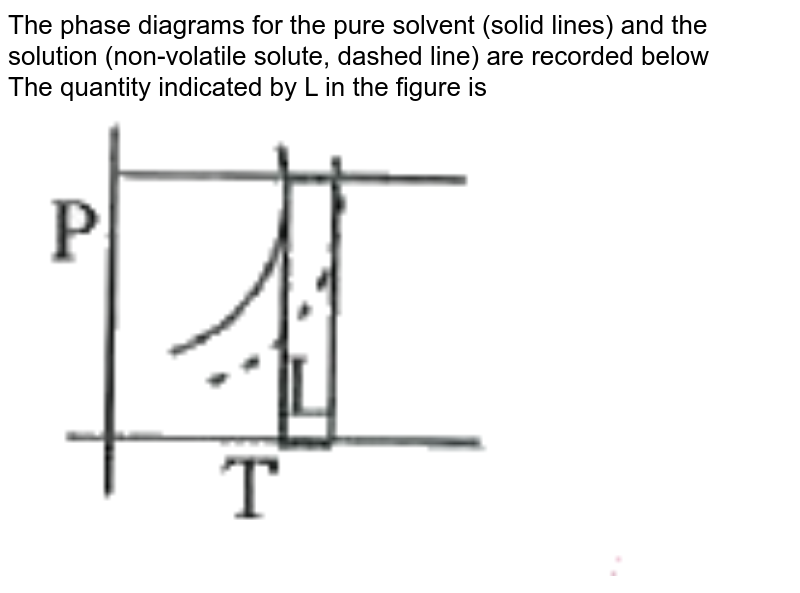
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the s... | Filo The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below : The quantity indicated by L in the figure is : A Δ p The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below. The quantity indicated by L in t ... NCERT Easy Reading Alleen Test Solutions Blog About Us Career. Course. NCERT. Class 12 Class 11 Class 10 Class 9 Class 8 Class 7 Class 6. IIT-JEE. Exam. Thermodynamic activity - Wikipedia Definition. The relative activity of a species i, denoted a i, is defined as: = where μ i is the (molar) chemical potential of the species i under the conditions of interest, μ o i is the (molar) chemical potential of that species under some defined set of standard conditions, R is the gas constant, T is the thermodynamic temperature and e is the exponential constant.
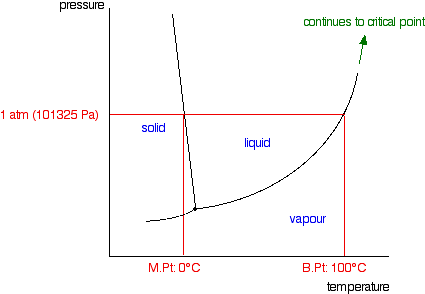
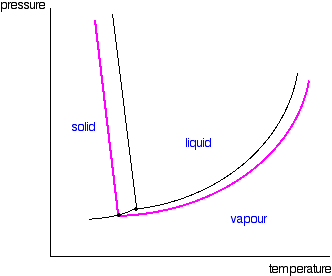
Phase diagram of pure solvent and solution. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › IronIron - Wikipedia Ferropericlase (Mg,Fe)O, a solid solution of periclase (MgO) and wüstite (FeO), makes up about 20% of the volume of the lower mantle of the Earth, which makes it the second most abundant mineral phase in that region after silicate perovskite (Mg,Fe)SiO 3; it also is the major host for iron in the lower mantle. en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Phase_(matter)Phase (matter) - Wikipedia Solubility is the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in a solvent before the solute ceases to dissolve and remains in a separate phase. A mixture can separate into more than two liquid phases and the concept of phase separation extends to solids, i.e., solids can form solid solutions or phase diagrams of pure substances - chemguide A phase diagram lets you work out exactly what phases are present at any given temperature and pressure. In the cases we'll be looking at on this page, the phases will simply be the solid, liquid or vapour (gas) states of a pure substance. This is the phase diagram for a typical pure substance. Azeotrope - Wikipedia A well-known example of a positive azeotrope is 95.63% ethanol and 4.37% water (by mass), which boils at 78.2 °C. Ethanol boils at 78.4 °C, water boils at 100 °C, but the azeotrope boils at 78.2 °C, which is lower than either of its constituents. Indeed, 78.2 °C is the minimum temperature at which any ethanol/water solution can boil at atmospheric pressure.
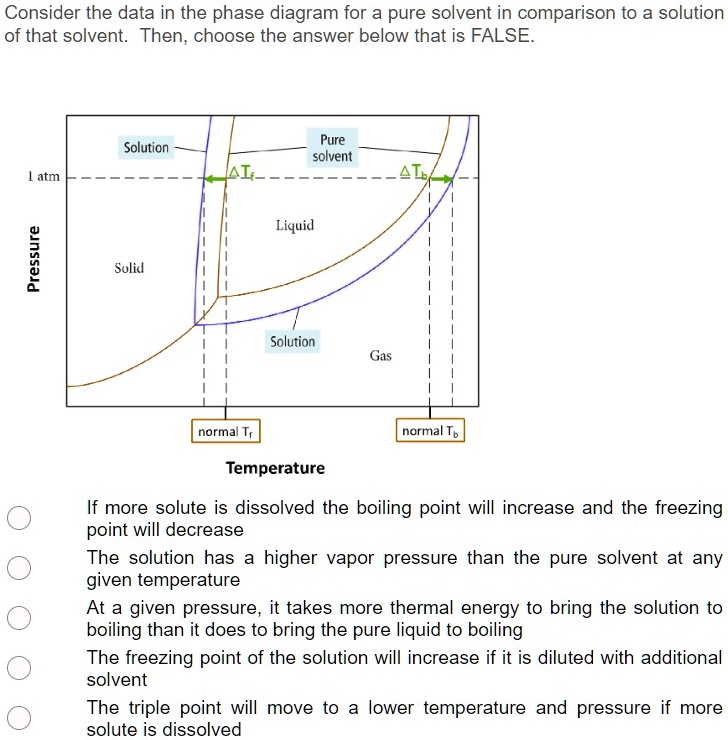
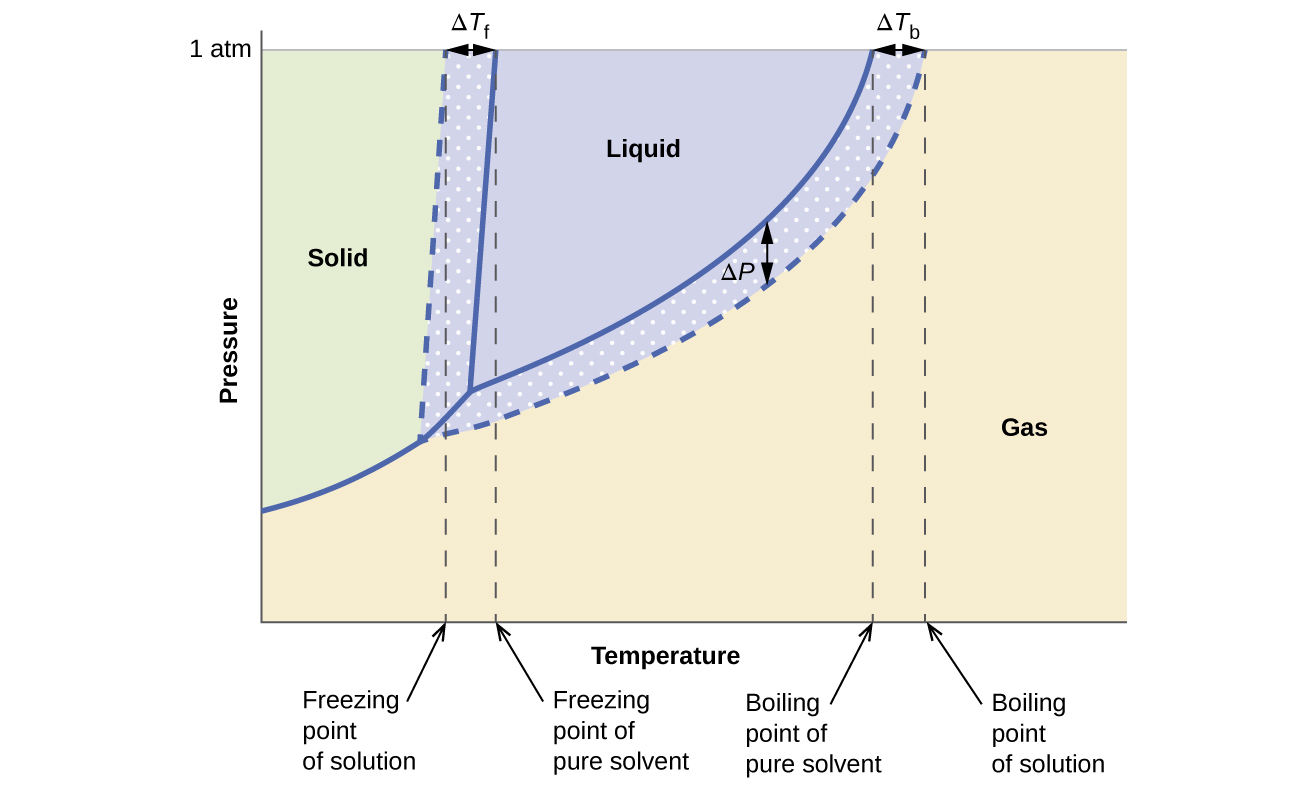
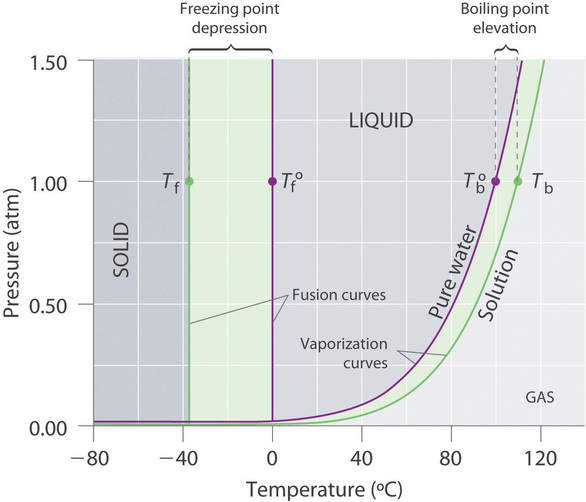
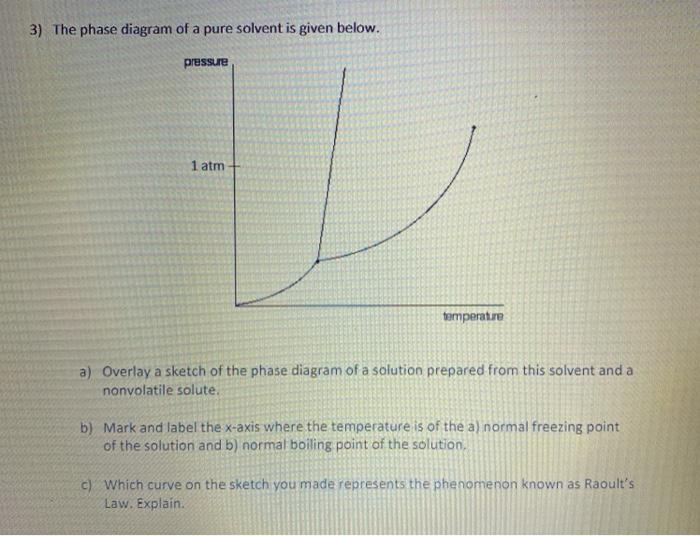
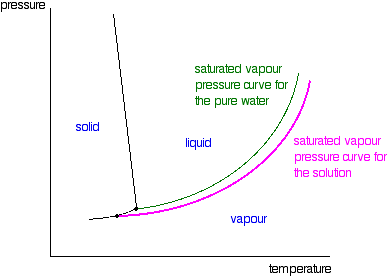
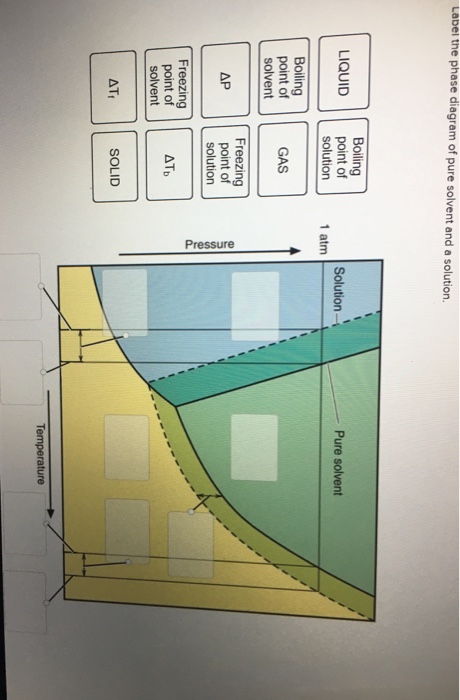
What are the most important differences between the phase di - Quizlet Two differences we can see on phase diagrams of a pure solvent and a solution are changes in phase transition temperatures \textbf{phase transition temperatures} phase transition temperatures.Solution will always have a higher boiling point \textbf{higher boiling point} higher boiling point and lower freezing point \textbf{lower freezing point} lower freezing point (check pages 501, 502). Solved Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a | Chegg.com Question: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. Freezing point of solution ΔΤ, Solution Pure solvent 1 atm Boiling point of solution SOLID LIQUID AP Pressure AT) GAS Boiling point of solvent Freezing point of solvent Temperature This problem has been solved! See the answer Show transcribed image text Expert Answer 100% (7 ratings) The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below: The quantity indicated by `L` i... Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution. The following phase diagram shows part of the liquid-vapor phase-transition boundaries for two solutions of equal concentration, one containing a nonvolatile solute and the other containing a volatile solute whose vapor pressure at a given...
Paper Chromatography: Is Black Ink Really Black? | Science Project The ink will be spotted onto strips of chromatography paper and put in a beaker containing a solution of alcohol and water. The paper (or more precisely the water that is adsorbed to the paper molecules) is the stationary phase and the alcohol and water solution is the solvent (mobile phase). The solvent will move by capillary action. The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below. The quantity indicated by L in the figure is: A. `Deltap` B. `DeltaT_(f)` C. `K_(b)m` D. `K_(f)m` en.wikipedia.org › wiki › EthanolEthanol - Wikipedia Absolute ethanol is used as a solvent for laboratory and industrial applications, where water will react with other chemicals, and as fuel alcohol. Spectroscopic ethanol is an absolute ethanol with a low absorbance in ultraviolet and visible light, fit for use as a solvent in ultraviolet-visible spectroscopy. › science-fair-projectsPaper Chromatography: Is Black Ink Really Black? | Science ... The ink will be spotted onto strips of chromatography paper and put in a beaker containing a solution of alcohol and water. The paper (or more precisely the water that is adsorbed to the paper molecules) is the stationary phase and the alcohol and water solution is the solvent (mobile phase). The solvent will move by capillary action.

The phase diagram for solvent and solutions is shown in the figure. What represents the normal boiling point of the solution?
Solid Solution Phase Diagram Labeled - label the phase diagram of pure ... Solid Solution Phase Diagram Labeled - 17 images - phase diagrams, practical maintenance blog archive phase diagrams part 2, practical maintenance blog archive phase diagrams part 2, thermodynamics flakes of ice in frozen milk and orange juice,
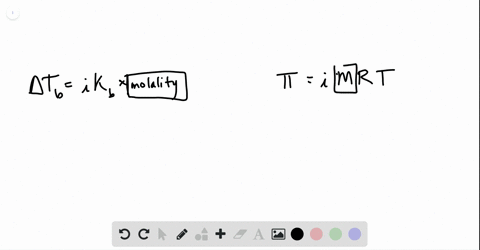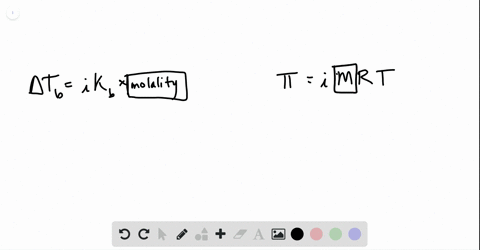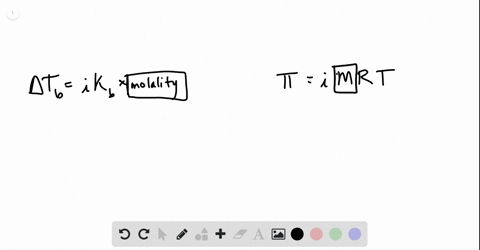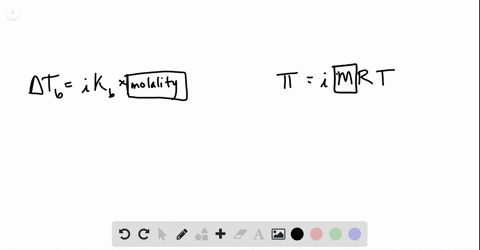
solutions, phase diagrams, colligative properties Flashcards | Quizlet S=KhP or s1/p1= s2/p2. Molarity. moles of solute/liters of solution. molality. moles of solute/kg of solvent. mole fraction. The ratio of the moles of solute in solution to the total number of moles of both solvent and solute. colligative properties. A property that depends only upon the number of solute particles, and not upon their identity.
Phase (matter) - Wikipedia Solubility is the maximum amount of a solute that can dissolve in a solvent before the solute ceases to dissolve and remains in a separate phase. ... An unusual feature of the water phase diagram is that the solid–liquid phase line (illustrated by the dotted green line) has a negative slope. ... For pure chemical elements, polymorphism is ...
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › Supercritical_fluidSupercritical fluid - Wikipedia Figures 1 and 2 show two-dimensional projections of a phase diagram. In the pressure-temperature phase diagram (Fig. 1) the boiling curve separates the gas and liquid region and ends in the critical point, where the liquid and gas phases disappear to become a single supercritical phase. The appearance of a single phase can also be observed in ...
Iron - Wikipedia Iron (/ ˈ aɪ ər n /) is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from Latin: ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table.It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in front of oxygen (32.1% and 30.1%, respectively), forming much of Earth's outer and inner core.It is the fourth most common …
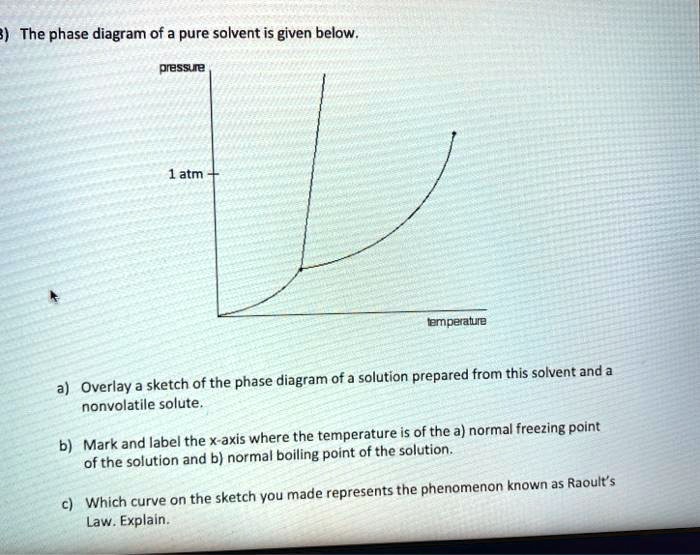
the phase diagrams for pure solvent and the solvent solution are shown identify the normal freezing pwolv and boiling bpsolv points for the pure solvent and the normal freezing fpsoln and bo 02333
Phase diagram - Wikipedia The simplest phase diagrams are pressure–temperature diagrams of a single simple substance, such as water.The axes correspond to the pressure and temperature.The phase diagram shows, in pressure–temperature space, the lines of equilibrium or phase boundaries between the three phases of solid, liquid, and gas.. The curves on the phase diagram show the points where the …
Phase and Phase System (Solution Solvent Solute) Differentiate between solvent and solute. Ans. Solution: A one phase homogeneous mixture of two or more kinds of different molecular or ionic substance is called a solution. Solvent. The component of the solution which is present in large quantity is called solvent. Solute . The component in small quantity is called a solute. Example: In a ...
Phase diagram of pure solvent and solution. - ResearchGate Phase diagram of pure solvent and solution. Source publication Design and Evaluation of Multiple Effect Evaporator Systems According to the Steam Ejector Position Article Full-text available Jan...
Ethanol - Wikipedia Ethanol (abbr. EtOH; also called ethyl alcohol, grain alcohol, drinking alcohol, or simply alcohol) is an organic compound.It is a simple alcohol with the chemical formula C 2 H 6 O.Its formula can be also written as CH 3 −CH 2 −OH or C 2 H 5 OH (an ethyl group linked to a hydroxyl group).Ethanol is a volatile, flammable, colorless liquid with a characteristic wine-like odor and …
en.wikipedia.org › wiki › SolubilitySolubility - Wikipedia In general, solubility in the solvent phase can be given only for a specific solute that is thermodynamically stable, and the value of the solubility will include all the species in the solution (in the example above, all the iron-containing complexes). Factors affecting solubility. Solubility is defined for specific phases.
Solved Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a | Chegg.com Expert Answer. 100% (138 ratings) This is …. View the full answer. Transcribed image text: Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution.
What Is a Hypertonic Solution? - Study.com Jun 29, 2021 · Any substance that is dissolved in a liquid solvent to create a solution is called a _____. _____ is an example of a solute that is needed by the body to function normally.
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below:
The figure representing the phase diagram of pure solvent and solution ... We have step-by-step solutions for your textbooks written by Bartleby experts! The figure representing the phase diagram of pure solvent and solution having non-volatile solute is given. An explanation for the change in the vapor pressure of the solution due to the presence of non-volatile solute that leads to lowering of melting point and ...
(Get Answer) - Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solution ... Phase Behaviour of t-Butane. Summarize the pressure/temperature combinations for the triple, freezing, and boiling points for t-butane and use these values to construct a phase diagram for this substance.
Label the phase diagram of pure solvent and a solutio… - SolvedLib Solitude in the information they want us to pull out is which line represents the solution. And what are the normal boiling points of a solvent in a solution? So let's break this down. We know we have a solvent, and we know we have a solution. Let's think about that where we heard about solvents and solutions before solutions.
Thermodynamic activity - Wikipedia Definition. The relative activity of a species i, denoted a i, is defined as: = where μ i is the (molar) chemical potential of the species i under the conditions of interest, μ o i is the (molar) chemical potential of that species under some defined set of standard conditions, R is the gas constant, T is the thermodynamic temperature and e is the exponential constant.
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution ... The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below. The quantity indicated by L in t ... NCERT Easy Reading Alleen Test Solutions Blog About Us Career. Course. NCERT. Class 12 Class 11 Class 10 Class 9 Class 8 Class 7 Class 6. IIT-JEE. Exam.
The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the s... | Filo The phase diagrams for the pure solvent (solid lines) and the solution (non-volatile solute, dashed line) are recorded below : The quantity indicated by L in the figure is : A Δ p



















Post a Comment for "39 phase diagram of pure solvent and solution"